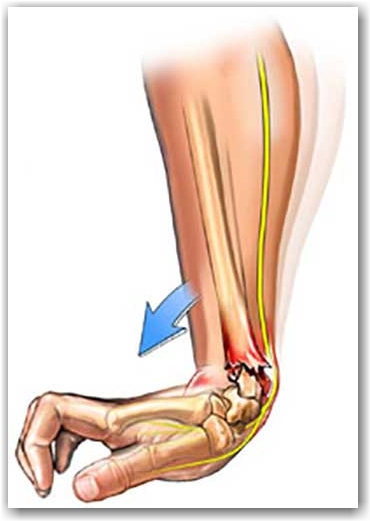
What and where is the wrist joint?
The wrist joint is one of the most complicated joints of the body consisting of the parts of 15 different bones; including joint surfaces of the lower part of the two forearm bones, 8 small wrist bones, and the bases of the metacarpal bones of the hand; and the tens of joint surfaces in between them. Due to this complicated structure of it, the wrist joint has a very wide joint motion range in 3D plane.
How can the wrist joint be broken?
- If somebody would fall down on an outstretched hand, fractures may occur in any of the wrist joint bones.
- Complicated, multi-fragmented, and severe comminuted fractures can be occurred in high-energy traumas such as traffic accidents or high fall injuries.
- Osteoporosis (fragility in bone structure) seen in older ages is one of the most common reasons of the wrist fracture which is generally simple and low energy ones.
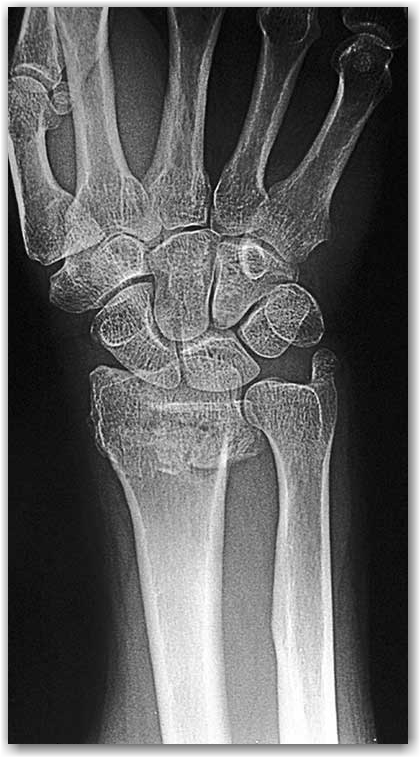
The most common wrist fracture is seen at the lower part of the RADIUS.
How do we know that our wrist is broken?
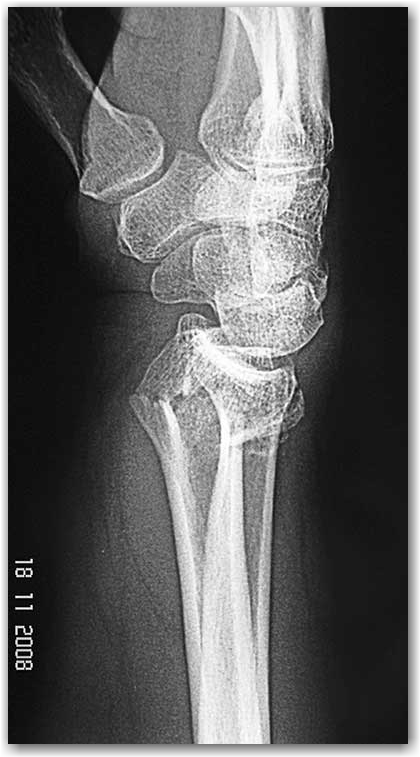
When any trauma is in subject such as falling down injury on an outstretched hand, there are generally swelling and pain around the wrist joint, limitation of range of motion of the joint, and difficulty and pain in using of the hand. The shape of your wrist is often disturbed. Some fractures are in simple fashion; however, some fractures may be fragmented, comminuted, displaced, and complicated in such a way to cause obvious deformity.
When the fractures that include joint surfaces cause irregularities or incongruities in the joint line, it will have features that adversely affect the future of the joint. If the fracture occurs with high-energy traumas accompanied with open wounds, it can lead to many complications, including infection.
Important points in wrist fracture
Every wrist fracture must be evaluated in detail using appropriate imaging modalities to understand every properties of the fracture. As well as x-ray evaluation which points only bony structure details, a wrist fracture may need advanced imaging techniques like computerized tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging to evaluate the soft tissue injuries. Because there is a possibility to get trauma all around the wrist joint, the individual integrity of all of the structures, which does not mean only the bone fracture, but also does surrounding ligaments, capsular soft tissues, tendons, muscles, and nerves, have to be determined.
The treatment of a wrist fracture
The treatment plan varies according to the position of the fracture, type, and configuration. The type of the treatment differs depending on whether the fracture position would be un-displaced and simple or displaced, comminuted, and complex in type. In addition, age of the patient, general health status, affected of dominant or recessive side, work and social life, concomitant injuries, associated with any other diseases or chronic systemic/local problems such as wrist arthritis are considered for planning the treatment.
- Treatment with a cast / splint application is possible if the fracture is not displaced or if it would be stable in a good position after reduction maneuver.
- Surgery may be required if the fracture is displaced and can not be reduced, or if it is too fragmented/comminuted, extending to the joint line.
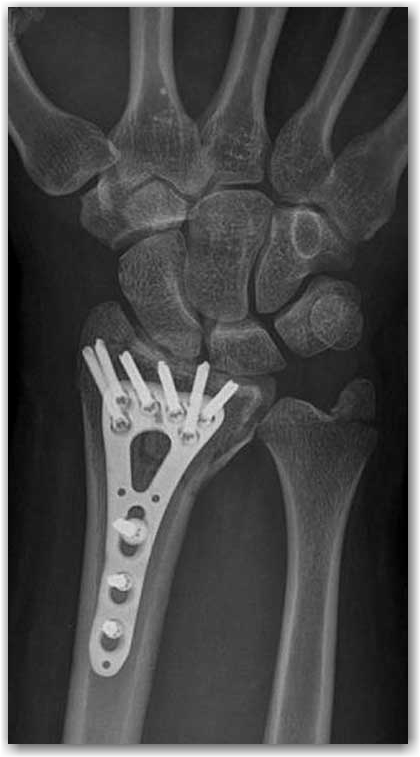
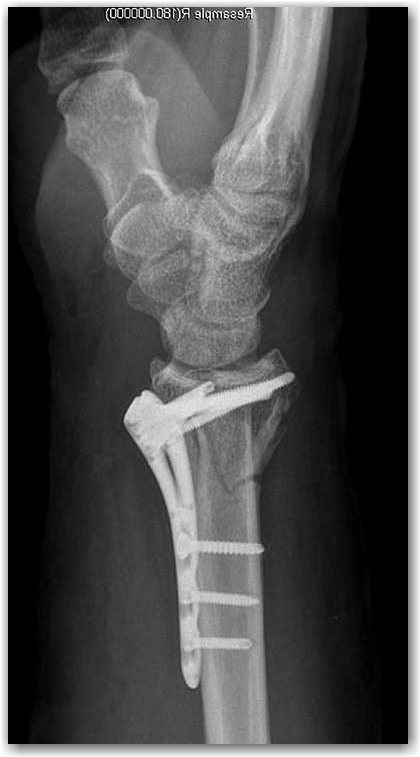
Surgical treatment of wrist fracture
In the surgical treatment, various nails/pins, screws, plate and screws, or devices called external fixators can be used to fix the fracture once the fracture is restored in its normal anatomical structure. Sometimes, endoscopic procedures such as wrist arthroscopy can be used to restore and control the joint congruity. The hand surgeon tries to choose the most appropriate treatment in a custom-made fashion according to the characteristics of each patient and the nature of the fracture. There may be bone deficiencies in the structure after the fracture has been restored in high-energy traumas that are very fragmented/comminuted, crushed, and complex fractures with a bone loss. In such cases, different bone substitutes (bone grafts) may be needed.
Prof. Dr. Eftal Güdemez
Orthopedics and Traumatology
Hand Surgery and Microsurgery